Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Physical Review B, 108(24), p.245110_1 - 245110_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We develop a mean-field theory of a novel Kondo effect emerging in systems without a Fermi surface, which instead emerges under strong magnetic fields. We determine the magnitude of the Kondo condensate, which is a particle pairing composed of conducting Dirac fermions and localized impurities. We focus on the competition between the Kondo effect and the energy gap formation that stems from the pairing among the Dirac fermions leading to the dynamical chiral symmetry breaking. We find that this competition induces a quantum critical point. We also investigate finite-temperature effects. This system at vanishing fermion density can be studied with Monte Carlo lattice simulations, which do not suffer from the sign problem.
Lee, S.*; Nakata, Koki; Tchernyshyov, O.*; Kim, S. K.*
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184432_1 - 184432_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate the interaction between magnons and a Skyrmion-textured domain wall in a two-dimensional antiferromagnet and elucidate the resultant properties of magnon transport. Using supersymmetric quantum mechanics, we solve the scattering problem of magnons on top of the domain wall and obtain the exact solutions of propagating and bound magnon modes. Then, we find their properties of reflection and refraction in the Skyrmion-textured domain wall, where magnons experience an emergent magnetic field due to its non-trivial spin texture-induced effective gauge field. Finally, we show that the thermal transport decreases as the domain wall's chirality increases. Our results suggest that the thermal transport of an antiferromagnet is tunable by modulating the Skyrmion charge density of the domain wall.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 107(7), p.074015_1 - 074015_15, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated, which is based on 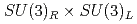 chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the
chiral symmetry and includes interactions between scalar and vector diquarks with one or two mesons. We find that the diquark interaction term with two mesons breaks the 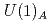 and flavor
and flavor 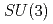 symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons
symmetries. To determine the coupling constants of the interaction Lagrangians, we investigate one-pion emission decays of singly heavy baryons 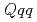 (
(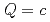 ,
,  and
and 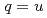 ,
,  ,
,  ), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
), where baryons are regarded as diquark-heavy-quark two-body systems. Using this model, we present predictions of the unobserved decay widths of singly heavy baryons. We also study the change of masses and strong decay widths of singly heavy baryons under partial restoration of chiral symmetry.
Hattori, Koichi*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 276, p.01015_1 - 01015_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.91(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)We investigate the QCD phase diagram in strong magnetic fields with heavy-quark impurities and determine the ground state within the mean-field analysis. The ground state is characterized by magnitudes of the pairing not only between the light quark and antiquark, i.e., chiral condensate, but also between the light quark and heavy-quark impurity, dubbed the Kondo condensate. We propose signatures of the interplay and/or competition between those two pairing phenomena reflected in the magnitude of the chiral condensate that is saturated with respect to the magnetic-field strength and anomalously increases with increasing temperature.
 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 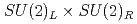 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 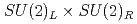 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 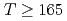 MeV.
MeV.
 3(111) and
3(111) and  5(0-13) grain boundaries of
5(0-13) grain boundaries of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Metals, 12(4), p.662_1 - 662_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus atoms in steels accumulate at grain boundaries via thermal and/or irradiation effects and induce grain boundary embrittlement. Quantitative prediction of phosphorus segregation at grain boundaries under various temperature and irradiation conditions is therefore essential for preventing embrittlement. To develop a model of grain boundary phosphorus segregation in  -iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries (
-iron, we studied the migration of a phosphorus atom in two types of symmetrical tilt grain boundaries ( 3[1-10](111) and
3[1-10](111) and  5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the
5[100](0-13) grain boundaries) using molecular dynamics simulations with an embedded atom method potential. The results revealed that, in the  3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the
3 grain boundary, phosphorus atoms migrate three-dimensionally mainly in the form of interstitial atoms, whereas in the  5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
5 grain boundary, these atoms migrate one-dimensionally mainly via vacancy-atom exchanges. Moreover, de-trapping of phosphorus atoms and vacancies was investigated.
Kim, Y.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074021_1 - 074021_17, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:93.07(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Energy spectrum of doubly heavy tetraquarks, 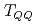 (
(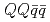 with
with 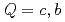 and
and 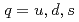 ), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the
), is studied in the potential chiral-diquark model. Using the chiral effective theory of diquarks and the quark-diquark-based potential model, the 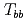 ,
, 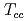 , and
, and 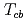 tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several
tetraquarks are described as a three-body system composed of two heavy quarks and an antidiquark. We find several 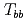 bound states, while no
bound states, while no 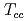 and
and 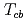 (deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the
(deep) bound state is seen. We also study the change of the 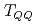 tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
tetraquark masses under restoration of chiral symmetry.
 anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperature
anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperatureAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(2), p.023B05_1 - 023B05_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The chiral susceptibility, or the first derivative of the chiral condensate with respect to the quark mass, is often used as a probe for the QCD phase transition since the chiral condensate is an order parameter of 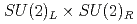 symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial
symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial  symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial
symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial  breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial
breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial  breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial
breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 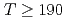 MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
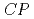 -violation studies on superheavy molecules; Theoretical and experimental perspectives
-violation studies on superheavy molecules; Theoretical and experimental perspectivesMitra, R.*; Prasannaa, V. S.*; Garcia Ruiz, R. F.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Abe, Minori*; Sakemi, Yasuhiro*; Das, B. P.*; Sahoo, B. K.*
Physical Review A, 104(6), p.062801_1 - 062801_9, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.51(Optics)We provide detailed theoretical studies of quantities relevant to the electron electric dipole moment (eEDM) and nucleus-electron scalar-pseudoscalar interactions in diatomic molecules containing superheavy lawrencium nuclei. The sensitivity to parity and time (or, equivalently, 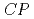 ) reversal violating properties is studied for different neutral and ionic molecules. The effective electric fields in these systems are found to be about 3
) reversal violating properties is studied for different neutral and ionic molecules. The effective electric fields in these systems are found to be about 3 4 times larger than other known molecules on which eEDM experiments are being performed. Similarly, these superheavy molecules exhibit an enhancement of more than 3 times for
4 times larger than other known molecules on which eEDM experiments are being performed. Similarly, these superheavy molecules exhibit an enhancement of more than 3 times for 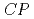 -violating scalar-pseudoscalar nucleus-electron interactions. Our preliminary analysis using the Woods-Saxon nuclear model also demonstrates that these results are sensitive to the diffuse surface interactions inside the Lr nucleus.
-violating scalar-pseudoscalar nucleus-electron interactions. Our preliminary analysis using the Woods-Saxon nuclear model also demonstrates that these results are sensitive to the diffuse surface interactions inside the Lr nucleus.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 104(9), p.094515_1 - 094515_11, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.61(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the Kondo effect with Wilson fermions. This is based on a mean-field approach for the chiral Gross-Neveu model including four-point interactions between a light Wilson fermion and a heavy fermion. For massless Wilson fermions, we demonstrate the appearance of the Kondo effect. We point out that there is a coexistence phase with both the light-fermion scalar condensate and Kondo condensate, and the critical chemical potentials of the scalar condensate are shifted by the Kondo effect. For negative-mass Wilson fermions, we find that the Kondo effect is favored near the parameter region realizing the Aoki phase. Our findings will be useful for understanding the roles of heavy impurities in Dirac semimetals, topological insulators, and lattice simulations.
Kim, Y.*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 104(5), p.054012_1 - 054012_18, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:73.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Chiral effective theory of scalar and vector diquarks is formulated according to the linear sigma model. The main application is to describe the ground and excited states of singly heavy baryons with a charm or bottom quark. Applying the potential quark model between the diquark and the heavy quark (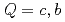 ), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of
), we construct a heavy-quark-diquark model. The spectra of the positive- and negative-parity states of 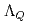 ,
, 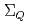 ,
, 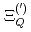 and
and 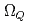 are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of
are obtained. The masses and interaction parameters of the effective theory are fixed partly from the lattice QCD data and also from fitting low-lying heavy baryon masses. We find that the negative parity excited states of 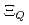 (flavor
(flavor 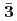 ) are different from those of
) are different from those of 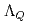 , because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand,
, because of the inverse hierarchy of the pseudoscalar diquark. On the other hand, 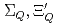 and
and 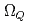 (flavor
(flavor 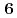 ) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
) baryons have similar spectra. We compare our results of the heavy-quark-diquark model with experimental data as well as the quark model.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.22(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 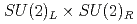 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
 5 grain boundary of
5 grain boundary of  -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.65 - 69, 2020/10
Phosphorus (P) is known as one of the elements which cause the grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steels and its GB segregation is promoted by the increase of vacancies and self-interstitial atoms due to irradiation. Thus we have been developing the rate-theory model for estimating GB P segregation under several temperatures and irradiation conditions. Because the model does not include the trapping and de-trapping processes properly, however, the model cannot calculate GB P coverage which is measured by experiments. As for the de-trapping process, so far, we have considered the migration of a P atom in the GB region of  3 symmetrical tilt GB using molecular dynamics (MD). In the current study, we also simulated the P migration in
3 symmetrical tilt GB using molecular dynamics (MD). In the current study, we also simulated the P migration in  5 GB using MD and compared the result with that of
5 GB using MD and compared the result with that of  3. As a result, at 800K, it was found that a P atom cannot migrate in
3. As a result, at 800K, it was found that a P atom cannot migrate in  5 without vacancies while a P atom can migrate between iron atoms in
5 without vacancies while a P atom can migrate between iron atoms in  3.
3.
 lattice QCD
lattice QCDSuzuki, Kei; Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.178_1 - 178_7, 2020/08
We investigate the high-temperature phase of QCD using lattice QCD simulations with 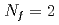 dynamical M
dynamical M bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial
bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial  symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M
symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial
bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial  anomaly at temperatures
anomaly at temperatures  220 MeV.
220 MeV.
Rohrhofer, C.*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Gattringer, C.*; Glozman, L. Ya.*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Lang, C. B.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.227_1 - 227_7, 2020/08
Properties of QCD matter change significantly around the chiral crossover temperature, and the effects on 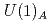 and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial
and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial 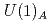 symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent
symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent 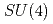 and
and 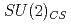 symmetries is discussed.
symmetries is discussed.
Kim, Y.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 102(1), p.014004_1 - 014004_9, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:75.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Applying the chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of singly heavy baryons. We introduce the phenomenological quark-model potentials for the confinement. We predict the charmed and bottom baryon spectrum showing the inverse mass hierarchy.
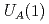 anomaly
anomalyHarada, Masayasu*; Liu, Y.-R.*; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 101(5), p.054038_1 - 054038_11, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.39(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Using a chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of diquark and heavy baryons consisting of diquarks. 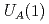 anomaly is considered in the chiral Lagrangian and its effects are studied.
anomaly is considered in the chiral Lagrangian and its effects are studied.
 -iron
-ironEbihara, Kenichi; Suzudo, Tomoaki
TMS 2020; 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, p.995 - 1002, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:59.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Phosphorus (P) is known as an element which causes grain boundary (GB) embrittlement in steels. In addition, GB P segregation is promoted by the increase of vacancies and self interstitial atoms due to irradiation. Thus, the diffusion rate theory model for estimating irradiation-induced GB P segregation has been developed based on the atomic processes. Since the present model does not include the trapping and de-trapping processes at GBs, however, it cannot calculate the value which is directly compared with experimental results. In this study, we simulated the migration of a P atom in the  3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
3(111) symmetrical tilt GB. In addition, by tracking the migration of the P atom, the diffusion barrier energy was evaluated. As a result, the diffusion barrier energy was almost the same as the P segregation energy of an interstitial site in the GB, and it was found that P atoms migrate via interstitial sites in the GB.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Horino, Koki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350(1), p.012183_1 - 012183_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Particles & Fields)As one of the advanced research and development for maintaining the stable operation of J-PARC RCS, we are developing semiconductor switch circuit for thyratron substitute adopted in kicker system. Radiation symmetric type circuits using semiconductors of SIC-MOSFETs are composed of circuits in which many semiconductor switches are multiplexed in parallel. Since the lengths of all parallel circuits are equal, the output waveform will not be distorted due to timing jitter or impedance. This circuit is useful for outputting the waveform of ultrafast short pulse. Therefore, we have developed a circuit that achieves further low inductance by making the power transmission circuit into a double circular ring structure equal to the coaxial shape. Compare the inductance value obtained from the structure and the output waveform. In addition, we compare the calculation and the measurement in the test and present the verification result of the developed circular ring structure.